The internet has become a part of all of our lives to the point where people who were raised on it cannot really imagine a life without it. Many of us have had our lives shaped heavily due to it, whether it comes to our relationships, jobs, or other areas. Yet perhaps the greatest benefit is best described by an Intel white paper originally published in 2009: “Broadband is not just infrastructure. It is a general-purpose technology that can fundamentally restructure an economy.”
And as time has gone on since 2009, that has only proven more true. The modern economy has been completely transformed by broadband connections and the development of faster internet (and just having internet access in the first place). Retail has become globalized to an extent. Specialty products and services can easily find their audience. We’ve had to rethink a lot of logistics. And that isn’t even talking about how the job market has changed as a result of broadband internet being available.
There is a lot to discuss, so keep on reading to learn more about the global online market:
What is Broadband Internet?
Before we go into detail about how broadband internet has affected all of us, we need to talk about exactly what broadband internet is and isn’t. Some misconceptions exist about it. It is a variety of technologies that allow for the simultaneous transmission of data along multiple bands. This allows for much faster transmission of information as compared to the dial-up internet that came before it.
The technology is incredibly interesting. In fact, it deserves its own article. Yet, for most intents and purposes, broadband internet can be used interchangeably with “high-speed internet.” Specifically, according to the specifications set by the FCC, broadband internet is a connection that exceeds 25 Mbps download speed, and 3 Mbps upload speed. Note, however, that this standard is considered outdated by many. There are calls to make the broadband standard higher to meet the average needs of people today (as opposed to years ago when the standard was last updated).

We mentioned broadband being a variety of technologies. Internet service providers use a variety of methods to provide broadband service to people. Current broadband options include:
- DSL broadband uses phone lines to transmit data (independently of telephone calls). It is one of the oldest forms of broadband, perhaps the most common. It is also, unfortunately, one of the worst in terms of speed and consistency. The speed can reach up to 100 Mbps download with commercial plans. However, it drops off based on the distance from the connection base. Upload speeds are among the worst, and most plans provide only 3-5 Mbps.
- Cable internet uses the wires for cable TV to provide internet service. It can provide great download speeds, usually several hundred Mbps for those willing to pay for it. Upload speeds are low, however. Additionally, there are consistency issues. Effectively, the more people use cable internet simultaneously, the more congestion can affect broadband speeds.
- Fiber optic broadband uses fiber optic wires transmitting pulses of light to carry information. It is currently the fastest form of internet service available in nearly every circumstance. The fastest plan we’ve seen with it is 6 Gbps, though generally, people will get fiber gigabit plans. Upload speeds can be simultaneous (so extremely fast), and speeds are consistent. Unfortunately, the fiber optic cables used are not installed as widely as cable or phone wires. Therefore, fiber broadband is generally only available in highly populated areas.
- Satellite (high altitude) broadband in the United States currently consists of ViaSat and HughesNet. Satellite internet has the ISP send a signal and route it through satellites. The signal is sent from the satellites toward the Earth. They provide download speeds ranging from 25 Mbps to 100 Mbps. However, actual speeds though can be quite a bit lower depending on hindering factors. Upload speeds are very slow, generally hovering around 3 Mbps. There is also the issue of extremely high latency. This type of broadband is unsuitable for gaming, video calls, and the like. Finally, there are usually data caps per month on usage. However, satellite internet is often still the best choice for people in rural or undeveloped areas that wouldn’t otherwise have broadband internet.
- Satellite (low altitude), which currently effectively consists of Starlink. While it is still getting off the ground in many areas, so to speak, so far, it has proven extremely promising, eliminating the high latency of high-altitude satellite broadband, and reaching speeds of up to 500 Mbps with some plans, along with decent (if not perfect) upload speeds. However, it is not available in many areas yet, there’s quite a long waitlist for it, and Starlink still needs to launch thousands of satellites.
There are also additional broadband technologies in development that are potentially on the way. You might have heard of quantum and laser broadband. However, at the moment, fiber internet is the fastest, most reliable, and generally offers the best price per Mb of download speed.
Why Broadband is Important
The internet is growing, and we are using it for more activities than ever. Even the average web page is larger in file size than ever before, given that graphics, potentially embedded videos, and audio are inserted into many pages. The internet is so much more than the mostly text-based pages that comprised it in the past.
On top of that, people are gaming, streaming content, and downloading large files regularly, and this trend is not likely to change. It is generally recommended to have at least a 25 Mbps download speed to stream 4K content. Video calls can require a 3 Mbps upload speed, depending on the client. And there are usually multiple processes and activities going on at the same time. Many households have more than one internet user in them. Modern modems and routers can easily handle many devices using the internet at once. Yet the bandwidth needs to be there. Good broadband internet makes this possible.
Essentially, the modern needs of the internet require that people have access to a broadband connection to properly access it. If someone doesn’t have it, they’ll find themselves at a disadvantage when it comes to working, their education, and just finding good entertainment online.
What Are the Benefits of Broadband Internet
It’s no question that broadband internet is a complete gain and benefit for anyone who has it. Yet how so? What are the exact benefits they can expect? What benefits does society at large gain? There are quite a few, and there’s a lot to talk about with just how many things can now be done online. Let’s talk about both the economic benefits and social benefits of broadband internet.
The Economic Benefits of Broadband
Let’s take another look at the message from the white paper for a moment: “Broadband is not just infrastructure. It is a general-purpose technology that can fundamentally restructure an economy.” We cannot overstate just how transformative broadband internet has been on the world economy. We cannot overstate it for the economy of every country that has it widely available. Broadband internet and its spread allow for more economic opportunities. People no longer need to live in a big city to have certain jobs., This decentralizes the economy and, in many cases, improves the quality of life of people, given the costs associated with living in a big city.

Broadband Internet’s Positive Effect on the U.S. Job Market
In the United States, investing just $10 billion in creating more broadband access would create around 500,000 new jobs. Think of the tax revenue that would come from those jobs. The access would, in some ways, pay for itself. It’s an investment that would not be easy and wouldn’t happen overnight, but it would pay off. Consider how broadband access has changed the areas where it already exists.
Where would this need to happen and where should expansion efforts be focused? Remote areas and rural regions are suffering the most when it comes to access. People living there need quality internet access as much as anyone else.
The question would remain how we bring broadband internet to these remote areas. Do we start laying cables to the areas, as much effort as that would take in those cases (there’s also maintenance to consider, often in semi-hazardous areas)? Or do we wait for Starlink and better satellite internet to take off? Broadband access will expand in its own time, but with intervention, the process could be sped up considerably, providing an incentive for ISPs to provide service to areas that they previously wrote off.
On the business side of things, broadband internet increases both productivity and efficiency. No more waiting terribly long to make sure that a page or file is downloaded. Communication becomes easier. Even something as simple as cloud storage has changed how we share information and collaborate in the (now often virtual) workplace.
Broadband’s Positive Effect Worldwide
While we’ve focused a lot on the United States, its effects on many developing nations and the rest of the world, in general, are profound.
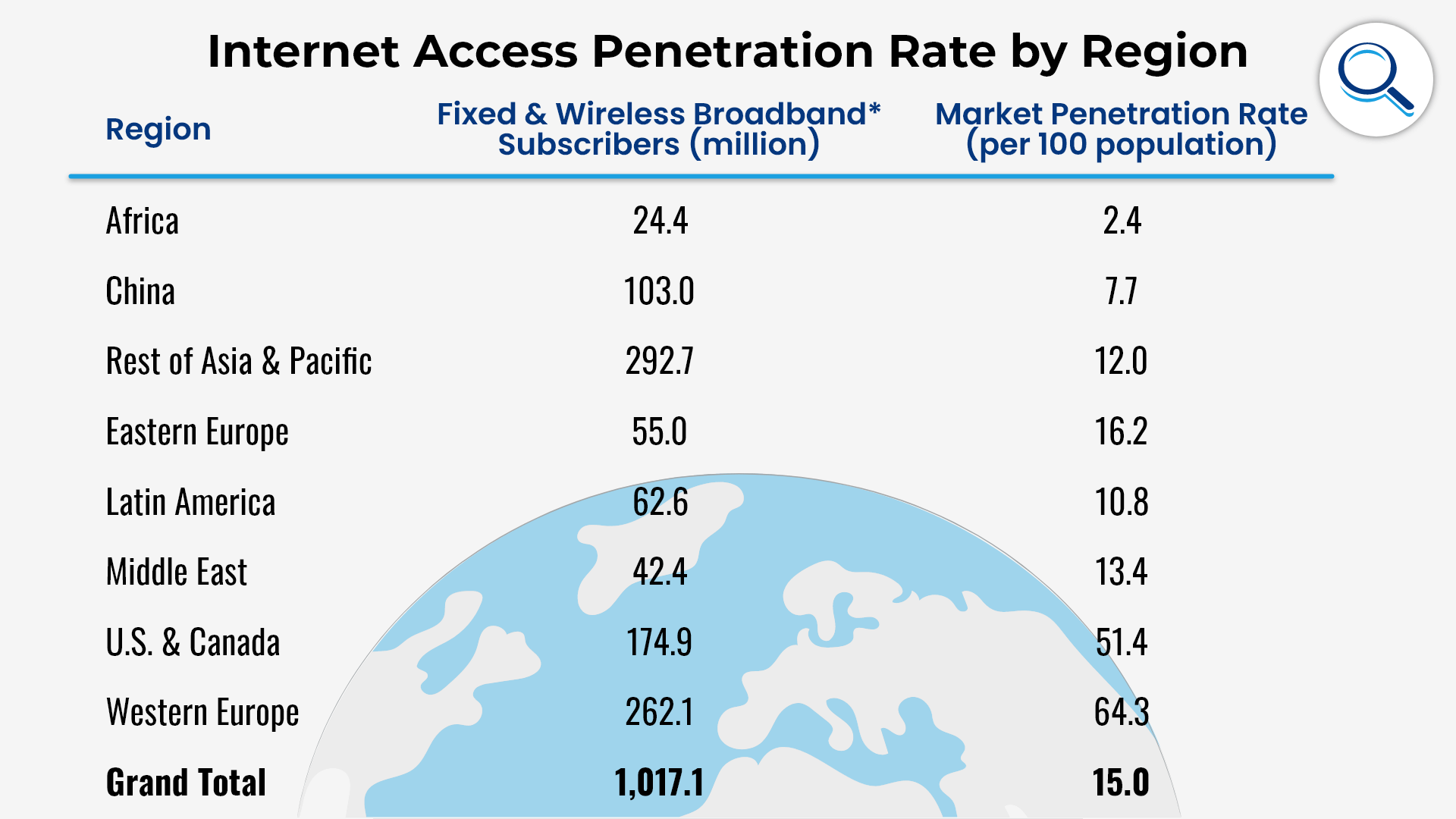
If you look at Latin America, a two percent increase in broadband market penetration would result in 378,000 new jobs. A two percent increase is not that difficult. It just requires the right investment and a solid infrastructure to work from. With proper planning and a bit of time, broadband can revolutionize the areas in terms of both the economy and education. That being said, Latin America is huge. It would still be a significant undertaking. It is possible that waiting for low-altitude satellite internet is the right option in this instance. This is especially the case for remote areas that getting lines to might be difficult.
And such a boost wouldn’t just help Latin American countries and the people who live there. It would have worldwide effects. It would provide new trade opportunities across the globe and potentially strengthen existing trade agreements and arrangements. It would increase the globalized workforce to some degree, allowing people with specialized skills to get jobs where they would best put to use. Similarly, it would keep specialized and skilled workers at home; otherwise, they might need to travel or migrate to find skilled workers.
And then there are decreased communication and potentially travel costs. Why fly someone halfway across the world for a meeting when it could be done virtually? Similarly, communication costs go down when free programs can replace international telephone charges. There is the cost of broadband internet, but for businesses regularly making such calls, broadband is much cheaper.
Finally, eCommerce has been one of the biggest boons for business in the last century, and broadband internet would open up those business models to poorer countries, potentially allowing them to sell and buy goods that otherwise wouldn’t find a market. This benefits all parties, assuming systems are in place for physical delivery (though strictly virtual services and trade can still help an area greatly).
Get Help Paying for Broadband with the Affordable Connectivity Program?
Broadband can be expensive. Though people in the United States with fewer means can get help with getting it with the Affordable Connectivity Program. Read the following to learn more:

What Is the Affordable Connectivity Program?
The affordable connectivity program was an effort to help people who are struggling financially to get access to broadband internet. It is an evolution of the relief efforts of the coronavirus and was previously known as the Emergency Broadband Benefit (perhaps you’ve heard of it or used it before). It pays $30 monthly for internet service for qualifying households, effectively acting as a discount on their bill. For households on tribal lands, it will pay $75 monthly. The benefit will also pay a one-time discount of $100 to help purchase a desktop, laptop, or tablet, giving families an easier time getting a device used to access broadband.
Qualifications for the Affordable Connectivity Program
To qualify for the Affordable Connectivity Program as of this writing, the following must be true:
- The intended recipient's household income is either at or below 200 percent of the Federal Poverty Guidelines.
One of the following must be true:
- The applicant has received a Pell grant during the current award year.
- The recipient meets the eligibility requirements for a participating provider’s existing low-income internet program (the exact details can vary from provider to provider).
- The applicant participates in other assistance programs such as SNAP, Medicaid, SSI, and/or others.
How to Enroll in the Affordable Connectivity Program
Enrolling is relatively simple. You can go to https://www.affordableconnectivity.gov/ to fill out an online form. Alternatively, you can use a printed version of the form and mail it out. This should give you a discount on your future plan.
Once this is done, you will want to contact your preferred provider and sign up for a plan. You will then have your discount applied. It should be noted that the exact method of application for the discount can vary from provider to provider. There might be an additional form or two for your to complete. Nonetheless, it should be relatively easy regardless of which provider you are working with.
Again, enrolling is not a terribly complex process. There are also frequent handouts and mailings about the program from ISPs and the government alike. These should tell you all the basic information as well. Additionally, should anything change about the program, you should be able to find out about it on the site.
What Are the Social Benefits of Broadband Internet?
Urbanization quickly leads to overpopulation in certain areas, and people living in big cities often have to deal with a lower quality of life because of it. For example, there are major problems in China and a few other countries as a result of this. However, since the big cities were where all the jobs were, people didn’t have much choice but to live in major urban centers, even if it wouldn’t be their first choice of lifestyle.

Broadband Internet Reduces Big City Problems by:
If people have broadband access, they’ll feel less pressure to move to urban areas. Some people might move to more populated areas simply because they are more likely to have internet access. In other cases, it is simply where the economic opportunities and jobs are.
Broadband access allows people to benefit from the educational advantages that the internet provides, and there are additional opportunities for people to learn more advanced and technical skills that would otherwise be hard to come by. This often results in improved income and a better quality of life.
Allowing more people to work from home in suburban or rural areas (assuming broadband is available there), reducing the overcrowding problem in big cities, reducing traffic, and allowing people living in all areas to enjoy a better quality of life. If more people can stay in rural areas who would like to, everyone benefits. People who enjoy the city or city life will still be able to go as they desire, just for fun instead of work obligations.
Equal Access to Education, Health, and Social Support
The internet provides access to information like never before and is so much more than social media and entertainment. It can help people learn new things, inspire creative ideas and bold endeavors, and simultaneously allow others around the world to connect with people. People need pillars of society to live their best lives and achieve their dreams. Broadband internet allows better access to those pillars.
Education, formal and informal, is one of the clearest benefits. Online colleges, universities, and training programs have provided millions of people with a chance to start a new and better career. And while not all are equal, and there are debates about the efficacy of online education compared to in-person models, people attest to its life-changing effects. And as education increases across the board, everyone benefits. Standards for training can increase across the board.
The need for broadband for social support was put on display during the pandemic lockdowns. People used the internet to keep in touch with others when travel and in-person visits were not an option. Zoom was used in ways to keep up connected, if imperfectly. Online parties were frequent, and they helped people who had little else to do. Families could keep in touch with each other, and people found communities online where they wouldn’t exist in their local areas. Broadband internet allowed for increased social support before the pandemic, and it is continuing to allow people to keep in touch and support each other afterward, especially when distance makes other communication difficulties.
And broadband can allow for some of the services that provide social support for millions. Informational campaigns can save lives. However, broadband allows access to telehealth and social support services. Many people cannot easily travel, for many reasons, to receive these benefits. They don’t really have opportunities to leave the home. With broadband internet, people can more easily access these services, vastly improving their health (mental and physical) and improving their overall quality of life.
How Broadband Internet Helps Developing Economies
We don’t need to look at just the United States to see the benefits of broadband internet. We don’t even need to look at just the developed world. Developing countries and economies actually have the most to gain from increased access and installation of broadband internet.
And note that entertainment is more than just entertainment: it often connects people to the outside world and introduced important and modern concepts. Streaming audio and video has enabled so much on its own. Meeting spaces such as Zoom are now available. There is a wealth of interactive apps that provide services or tools that are too many to mention here.
Perhaps it brings the most potential benefit to online entrepreneurs. They otherwise would have great ideas but not the means to get them off the ground. All they lack is reliable internet service. The people now willing to put in the effort and intellectual labor to make their online business happen can succeed if they have a broadband connection. This is the case no matter where they happen to be from.
Essentially, broadband internet allows people to find better careers and allows them to pursue those careers in a wider array of areas due to the benefits of remote work. There are also economic benefits, a vast array of helpful information to find, and the ability to connect with others and entertainment alike. Broadband is one of the clearest ways for people to improve their quality of life. And even if people already have broadband, there are benefits for them if access is expanded to more people.
The Bottom Line
The benefits of broadband internet are hard to keep track of, if only because so many of them exist. But by expanding broadband access, countries and organizations can easily create more jobs. They can help advance developing economies and provide social benefits to millions (if not billions) at an extremely low cost compared to the return. It creates educational opportunities (self-directed or not) for many. And it provides people with access to products, services, and information they otherwise would never hear about.
Broadband internet has become essential in daily life in just two decades. It leaves us to wonder what might be next for the technology or what innovations using our new connectedness we might see in the near future. Thank you for reading. We encourage you to bookmark and come back to this page as you feel the need.
FAQ
When Will the Affordable Connectivity Program End?
We aren’t certain. As of this writing, the ACP is meant to be a long-term program with no set end date. The government guaranteed $14 billion to the program, which is expected to last at least as long as that money remains. Some estimate that the money will last at least until 2024. And there is always the possibility that the program will change, be extended, or something else in the coming years.
How Much Does Broadband Internet Cost?
Broadband internet services generally cost between $40 and $120 a month. However, given that services can be part of bundles, be subject to temporary or more permanent discounts, and there can be additional charges for equipment, among other things, this price can still vary further. However, it ultimately comes down to the quality of service one wants to get and the local competition.
What Is a Broadband Internet Connection and How Does It Work?
A broadband internet connection is generally provided by an internet service provider that utilizes a technology that allows for rapid data transmission. This transmission turns into an internet connection.
As for how it works, it can vary. Usually, however, it uses multiple bands in a cable or uses radio waves to rapidly transmit information. This often takes the form of pulses of light or signals until a modem translates those. Compared to the previously available dial-up internet, it is a major leap forward and provides plenty of opportunities for further improvement.
Is a Broadband Connection Better than Fiber?
The two aren’t really comparable. Fiber internet is a type of broadband connection. Broadband is a group of technologies that utilize different types of wires and signals to transmit information. Namely, this is the internet. Fiber is a form of connection that uses fiber optic wires comprised of many tiny plastic or glass strands to transmit information. However, fiber is effectively the fastest and best form of broadband connection we have today. If you’re comparing it to nearly any other type of broadband service, fiber would be better.
What Is the Difference Between Broadband Internet and WiFi?
Broadband internet is a series of methods and technologies that allow for the rapid transmission of data that comprises the internet. Your ISP provides it. It is what you pay for when you order internet service. Broadband is effectively your internet connection. It and a modem are what you need if you’re fine with just a wired connection.
WiFi is a network in a limited area that uses radio waves to connect devices in your home. To create a WiFi network that can connect to the internet, you need a broadband connection as provided by an internet service provider. Essentially, you need broadband internet to have WiFi. WiFi connects your home wirelessly to the internet. Both are all but necessary in today’s world.
